One of the key priorities while setting up your blog is to decide on your blog’s URL structure for the individual posts. An improper URL structure can impact the performance of your blog, or not be tuned well for SEO. This article deals with some of the commonly used URL structures and helps you select the right one for your blog.
What is a Permalink?
Permalink (short for “permanent link”) is a URL that points to a particular post or entry in your blog. The home page URL of a blog usually links to a dynamic page where posts are published. This is because as new entries are posted in the blog, the previous ones gradually stack up and eventually move to the next page. A permalink, on the other hand, links to an individual blog post. This link remains unchanged (hence permanent) irrespective of any updates to a blog’s content. Permalinks can be used share individual posts universally and also bookmark them.
Why are Permalinks important?
Permalink structure is one of the key factors to consider while setting up your blog. Since permalinks are static URLs in a dynamic website, they are usually managed and maintained by a database – linking each URL to the actual page containing the post. A well-structured permalink will take less time to search the database and hence will result in a better site performance.
Public blogs attract maximum traffic from web searches performed by users. A Permalink structure also determines how well your posts are ranked in various web search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc.) for relevant search terms. If not optimized, a permalink structure may impact the ranking of pages in your blog. However, various other conditions also determine the ranking of a page; permalink is one of them.
Finally, a well-structured permalink is user friendly, compact and easier to understand. It should not contain any unnecessary and meaningless characters.
Performance versus SEO
These two factors lie on opposite ends of each other, and both are equally important. Tuning your blog for better performance might give you a negative impact on SEO. Permalinks are also a part of this battle. A permalink structure which is good for SEO might have to compromise for the blog’s performance, (although recent updates in WordPress has eliminated the need for such a compromise). An ideal permalink structure will maintain a fine balance between Performance and SEO.
Most newcomers in the blogosphere are unaware of the impacts of a proper permalink structure. Later when they face issues in performance and/or SEO (Search Engine Optimization), they tend to modify their permalink structure. However, there are several downsides of altering an established permalink structure. One of the major ones being the fact that your site pages will lose its previously gained PageRank value. Secondly, all externally shared links to individual articles will become invalid and produce 404 Page Not Found Error unless the links are properly handled.
The Right Permalink Structure
So, now you may ask, “What’s the most convenient permalink structure?” Well, there have been various debates in the past regarding the same question and different experts express different opinions about it. But the most convenient URL structure for a blog depends largely on the type of blog being maintained. The following are a few of the recommended permalink structures for different types of blogs.
1. Genre blogs
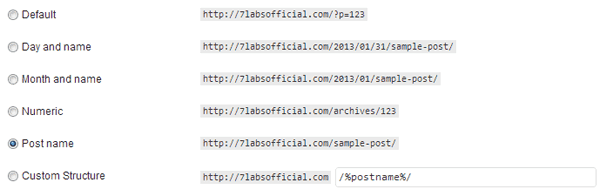
Permalink Structure: /%postname%/
Example URL: www.example.com/sample-post/
Say you want to write a cookbook blog, or want to write articles regarding pet care; for writing more focused contents on your blog, this type of permalink structure will suit you best. Such URL structures are usually good for SEO. Choose a suitable title that contains possible search keywords. That way, the URL will also include them, hence optimizing the URL for better search results.
2. Topical Blogs
Permalink Structure: /%category%/%postname%/
Example URL: www.example.com/category/sample-post/
If your blog features subjective topics and cover a wide variety of articles, it is best to put the articles into separate categories and tag them to specific keywords. If you now create a URL structure containing the category/tag along with the post title, it will be more understandable and user friendly. Such permalinks also tend to be more optimized as they may help search engines like Google to categorize pages and produce more relevant and useful results.
3. News Blogs
Permalink Structure: /%year%/%monthnum%/%day%/%postname%/
Example URL: www.example.com/2013/01/31/sample-post/
News blogs generally cover topics related to current incidents (like daily news websites). The stories published in such type of blogs usually bear importance for a short period of time. If you are running a news blog, it is better to go for a permalink structure that contains date information. Search engines like Google sometimes use this information to filter out current articles and place them at a higher rank for a short term. However, if you write articles where the information provided might be useful to readers in the long term, this permalink structure is not good for you, as readers could consider the information as outdated.
Note: Additionally, Google requires at least 3 digit number in the permalink to be featured in Google News. For this you can append a post ID along with the title in the permalink, but in this case the first 99 posts would not be considered as news.
Custom Structure: /%year%/%monthnum%/%day%/%postname%/%post_id%
Check the Requirements of Getting into Google news
4. Private Blogs
Permalink Structure: Default
Example URL: www.example.com/?p=123
If you don’t want to target incoming users from various search engines, the default permalink structure of WordPress is the most suitable for you. Being short and unique, it is the most performance-friendly structure, since WordPress doesn’t have to look for any additional information while searching a particular page. Also, since you won’t target any search traffic into your blog, you don’t need to worry about SEO too much.
Notes:
1. Including extensions in permalinks: If you want to end permalinks with the post name, it is a good practice to append the .html extension to it. File extensions help Google to determine the type of file. In this case, Google knows the particular URL directs to an HTML page and hence would contain text based web content.
2. Depth of URL: Choose a permalink structure that looks decent. It is preferable not to go too deep down along multiple levels (using slashes ‘\’) in a permalink. Usually, a permalink going two to three levels down should be fine. But a permalink with a depth of more than 3 levels doesn’t look too user friendly. Additionally, Google may not worry much about URL depths, though it may impact searches on other engines like Bing or Yahoo.
3. Length of the slug: A “slug” is the part of an URL that points to a particular web page in a blog. Try to use a short permalink which is a stripped down version of the post title containing some relevant keywords only. This produces a search optimized URL which is user friendly too. Slug length should not exceed four to five words.
4. Variables within the permalink: Previously, including a variable text field like post name or category within the permalink caused serious performance issues when the blog had a large number of pages. As of WordPress 3.3, this issue has been fixed and post names included within permalinks does not take any significant performance hit. Make sure you are using the latest version of WordPress to stay up to date with all major and minor bug fixes.
How to set up permalinks
You can set up or change your blog’s permalink structure by logging into Dashboard and going to Settings >> Permalinks. Choose from a given set of predefined permalinks or define your own(Custom Structure). The following WordPress guide describes the different mnemonics used in permalink structure definitions.
Using Permalinks << WordPress Codex
Planning to change your blog’s URL structure? First try to determine how badly does your current structure really impacts SEO and performance. If you need to change the structure, don’t forget to take care of all your broken links. Use proper 301 Redirects to divert all your broken links to their respective updated URLs. If you need assistance on how to redirect URLs, just keep following us. We’ll discuss URL redirection in detail in another chapter.