What is a Residential IP
Residential IP is a public IP address assigned to a home user by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) while connected to the Internet. It is the IP address that cellular (e.g., smartphones) or networking (e.g., home routers) devices receive from the users’ ISPs.
Residential IPs are owned by ISPs (such as Verizon, AT&T, Spectrum, etc.), and due to the significant adoption of Internet services among home users around the world, these IP addresses are available from almost any location.
What is a Datacenter IP
A Datacenter IP is an IP address belonging to a specific range of IPs assigned to a data center. Datacenter IPs are usually owned/managed by large entities (companies, organizations, etc.).
These IP addresses are only available from specific regions or locations where data centers are set up. Thus, datacenter IPs usually have a limited choice of locations, compared to residential IPs.
Datacenter IPs are usually owned by cloud service providers such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and other major corporations that maintain their own data centers.
Residential & Datacenter IP in the context of VPN & Proxy
Many VPN & Proxy service providers give an option to choose between Datacenter or Residential IP. This IP acts as a client IP to the internet and masks the actual client public IP address granted by ISP. You can read more on VPN & Proxy in our previous articles.
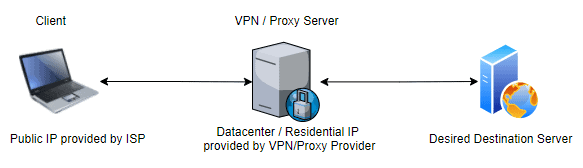
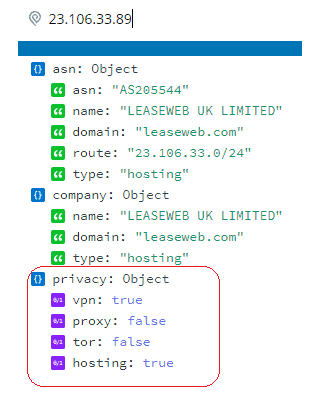
When someone uses a consumer-grade VPN or proxy service, they would most likely get a datacenter IP address. Datacenter IP Proxies/VPNs generally have faster response times and are cheaper, but they also have a high probability of getting blocked by websites and services. Websites or servers intending to blacklist VPNs or Proxies can use services like IPInfo to block VPN/Proxy specific IPs.
On the other hand, Residential IP Proxies/VPNs are costlier and harder to block by websites and services but usually have slower response times. This is because Residential IPs belong to some ISP, and not to a dedicated data center.
But why would anyone use a residential IP when they are relatively slow and expensive?
Residential IPs are in fact used by data mining companies, who use automated bots to scrape information from websites and use it for market research, business automation, retail price tracking, and more. As they need frequently rotating IP addresses that are difficult to block.
With Residential IPs, data miners can drive bots to target websites to scrape information and make it look like regular traffic from normal users.
A few popular Residential IP providers include GeoSurf, Oxylabs, SmartProxy, etc.